Unraveling the Fainting Mystery: Exploring Gender Differences in Syncope
Related Articles: Unraveling the Fainting Mystery: Exploring Gender Differences in Syncope
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Fainting Mystery: Exploring Gender Differences in Syncope. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Fainting Mystery: Exploring Gender Differences in Syncope

Fainting, or syncope, is a common experience, characterized by a temporary loss of consciousness due to a sudden drop in blood flow to the brain. While it can be a frightening event, fainting is generally harmless and usually resolves on its own. However, the perception persists that women faint more frequently than men. This article delves into the intricacies of fainting, examining the scientific evidence surrounding gender differences in syncope occurrence and exploring the underlying physiological and social factors that may contribute to this perceived disparity.
The Prevalence Puzzle: Examining the Data
Studies have consistently shown that women report experiencing fainting episodes more often than men. This observation, however, is not necessarily indicative of a true biological difference. Several factors contribute to this perceived discrepancy, complicating the interpretation of available data.
- Reporting Bias: Women tend to be more likely to seek medical attention for fainting episodes, potentially leading to a higher reported incidence. Societal norms often encourage women to express vulnerability and seek help, while men may be more inclined to downplay or even hide their symptoms.
- Hormonal Influences: The female hormonal cycle, particularly during menstruation and pregnancy, can influence blood pressure and vascular reactivity, potentially increasing susceptibility to fainting. However, the precise mechanisms and the extent to which hormones contribute to fainting remain unclear.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as anemia, autonomic dysfunction, and heart conditions, can predispose individuals to fainting. While these conditions are not inherently gender-specific, their prevalence may differ between genders, contributing to the perceived higher incidence of fainting in women.
- Social and Environmental Factors: Stress, anxiety, and certain medications can also trigger fainting. These factors may have different social and environmental influences on women and men, potentially impacting their likelihood of experiencing syncope.
Exploring the Physiological Mechanisms
Fainting is primarily triggered by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain, leading to a temporary loss of consciousness. This decrease can be caused by various factors, including:
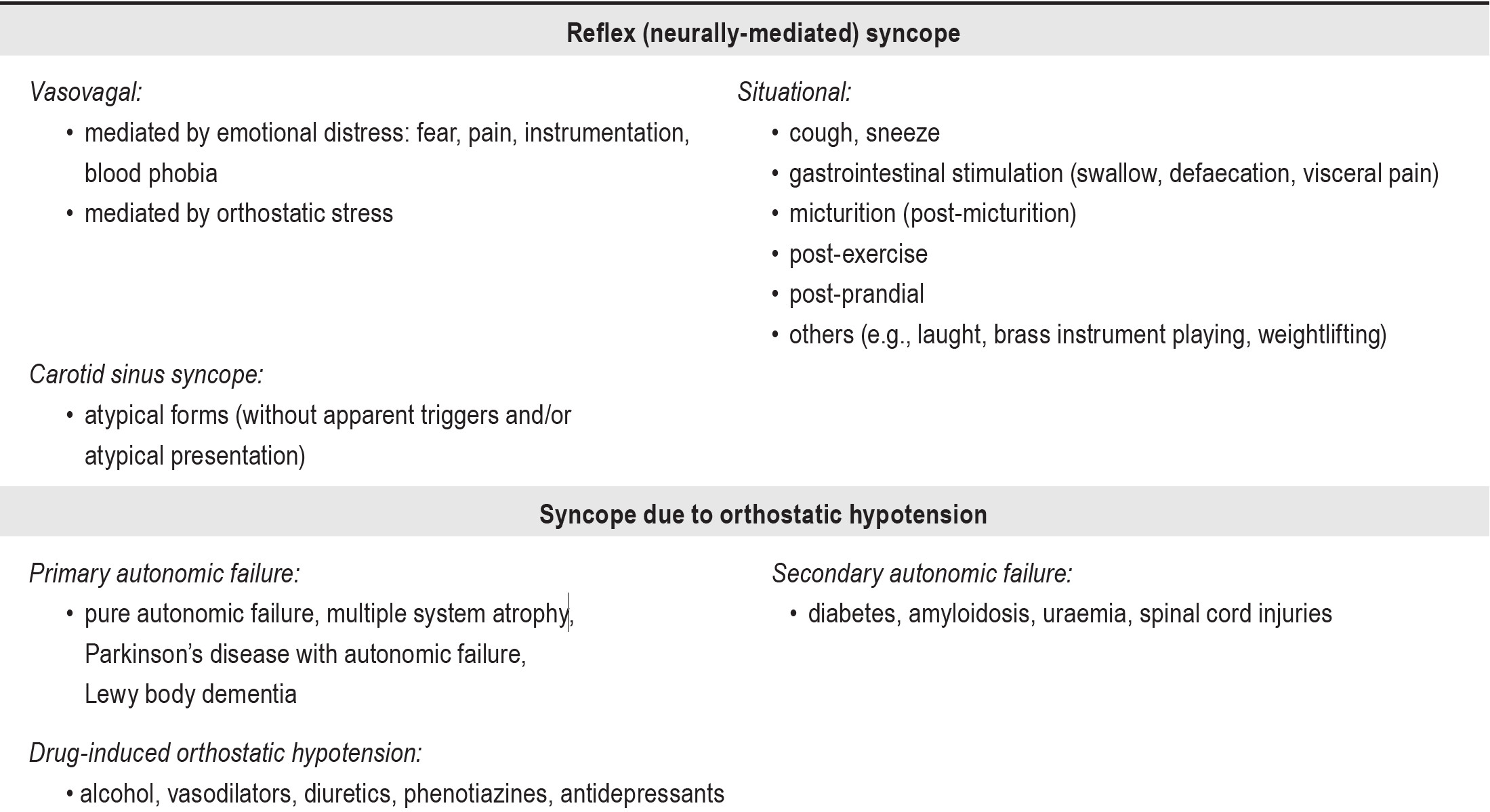
- Vasovagal Syncope: This is the most common type of fainting, often triggered by emotional stress, pain, or prolonged standing. It involves a rapid decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, caused by a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood pressure and heart rate.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: This occurs when blood pressure drops significantly when standing up, leading to reduced blood flow to the brain. It can be caused by dehydration, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions.
- Cardiac Syncope: This type of fainting is caused by problems with the heart, such as arrhythmias or heart valve disease, which disrupt the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
- Neurological Syncope: Certain neurological conditions, such as seizures or migraines, can also cause fainting.
While the underlying physiological mechanisms of fainting are similar for both genders, subtle differences in hormonal regulation, vascular reactivity, and autonomic nervous system function may contribute to variations in fainting susceptibility.
The Importance of Understanding Gender Differences
Recognizing potential gender differences in fainting is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment: Understanding the factors that may contribute to fainting in women can help healthcare professionals make more accurate diagnoses and provide tailored treatment plans.
- Reducing Stigma: Addressing the perception that fainting is more common in women can help reduce stigma associated with the condition and encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment.
- Promoting Health Awareness: Raising awareness about fainting and its potential causes can empower individuals to take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce their risk of experiencing syncope.
FAQs about Fainting and Gender
Q: Is it true that women faint more than men?
A: While women report experiencing fainting episodes more often, this may be due to reporting bias, societal norms, and other factors rather than a true biological difference.
Q: What are the main causes of fainting?
A: The most common cause of fainting is vasovagal syncope, triggered by emotional stress, pain, or prolonged standing. Other causes include orthostatic hypotension, cardiac syncope, and neurological conditions.
Q: Are there any hormonal influences on fainting in women?
A: The female hormonal cycle, particularly during menstruation and pregnancy, can influence blood pressure and vascular reactivity, potentially increasing susceptibility to fainting. However, the exact mechanisms and extent of this influence are not fully understood.
Q: What should I do if I faint?
A: If you faint, it is important to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying medical conditions. You should also consult with your doctor if you experience frequent fainting episodes.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent fainting?
A: Yes, several lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of fainting, including:
- Staying hydrated: Dehydration can contribute to orthostatic hypotension.
- Avoiding prolonged standing: Prolonged standing can trigger vasovagal syncope.
- Managing stress: Stress can trigger fainting.
- Eating regular meals: Low blood sugar can lead to fainting.
- Getting enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can contribute to fainting.
Tips for Managing Fainting
- Keep a fainting diary: This can help identify potential triggers and patterns.
- Consult a healthcare professional: If you experience frequent fainting episodes, seek medical advice to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
- Follow your doctor’s recommendations: If you are diagnosed with a medical condition that can cause fainting, follow your doctor’s treatment plan.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Stress management techniques can help reduce the risk of fainting.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can contribute to fainting.
- Avoid triggers: If you know what triggers your fainting, try to avoid those triggers.
Conclusion
While the perception persists that women faint more than men, the reality is more complex. While women may report fainting episodes more frequently, this is likely due to a combination of factors, including reporting bias, societal norms, and potential hormonal influences. It is important to recognize that fainting can affect both genders and that accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing this condition effectively. Further research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms of fainting and the role of gender in its occurrence. By promoting awareness and understanding of fainting, we can empower individuals to take control of their health and seek appropriate medical care when necessary.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Fainting Mystery: Exploring Gender Differences in Syncope. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
