The Impact of Rapid Fashion Consumption: A Critical Examination
Related Articles: The Impact of Rapid Fashion Consumption: A Critical Examination
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Impact of Rapid Fashion Consumption: A Critical Examination. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Impact of Rapid Fashion Consumption: A Critical Examination

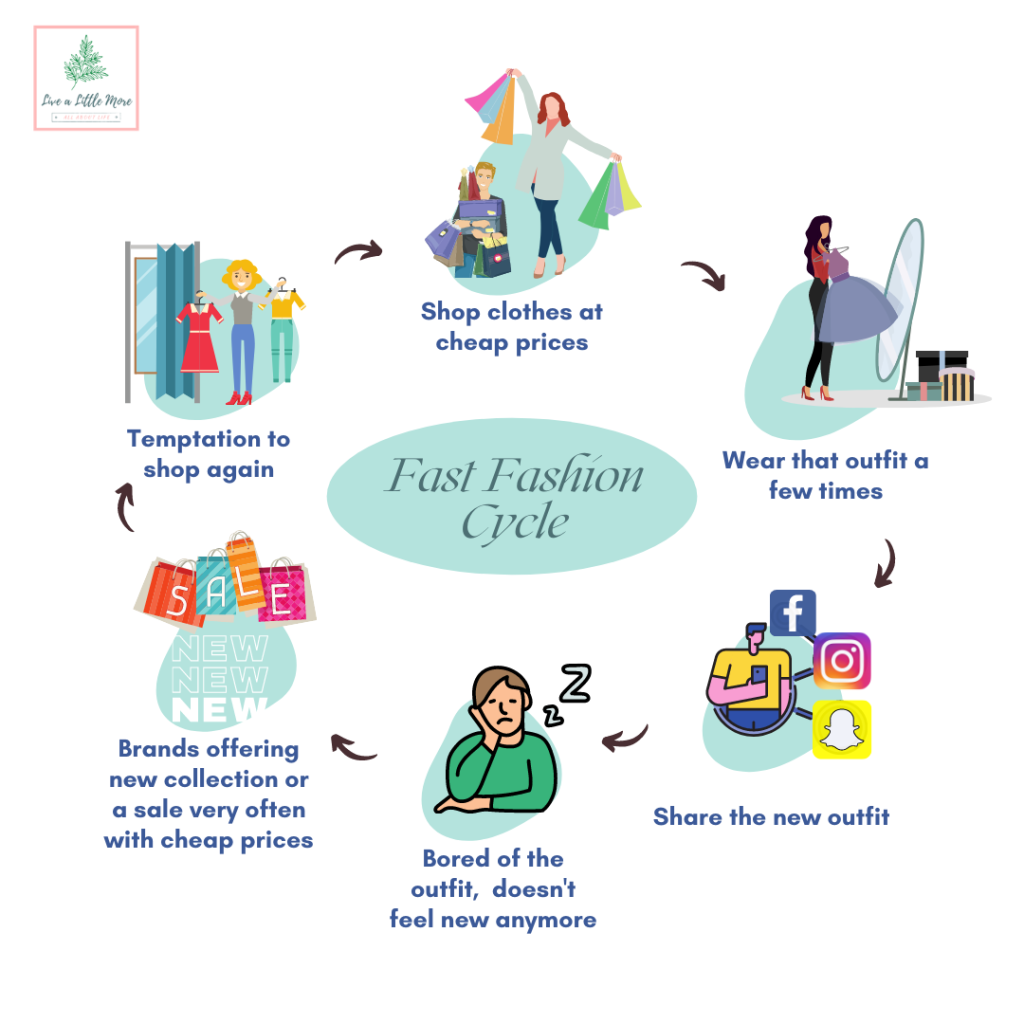
The relentless pursuit of the latest trends, fueled by the insatiable appetite for novelty and affordability, has given rise to a phenomenon known as "fast fashion." This pervasive industry model, characterized by rapid production cycles, low prices, and frequent trend updates, has profoundly impacted the global landscape, leaving an indelible mark on environmental, social, and economic spheres.
Environmental Consequences:
The environmental footprint of fast fashion is substantial and multifaceted. The industry’s reliance on synthetic fibers, particularly polyester, poses a significant threat to the environment. Polyester, derived from petroleum, is non-biodegradable and releases harmful microplastics into the environment during washing and disposal. These microplastics contaminate water sources, infiltrate the food chain, and ultimately impact human health.
Furthermore, the production of textiles necessitates substantial water consumption. Cotton, a staple fiber in clothing production, is a water-intensive crop. The dyeing and finishing processes involved in textile manufacturing further exacerbate water pollution, releasing toxic chemicals into water bodies.
The environmental impact extends beyond water consumption. The production of garments, from fiber extraction to transportation, generates significant carbon emissions. The global fashion industry is estimated to be responsible for 10% of global carbon emissions, exceeding the combined emissions of all international flights and maritime shipping.
Social Implications:
The social implications of fast fashion are equally alarming. The industry’s emphasis on low prices often translates into exploitative labor practices. Garment workers, predominantly women, in developing countries face low wages, unsafe working conditions, and long hours. The relentless pursuit of speed and efficiency in the supply chain leaves little room for worker rights and fair labor practices.
Fast fashion also contributes to the perpetuation of unsustainable consumption patterns. The constant bombardment of new trends and the allure of low prices encourage consumers to buy more clothes than they need, resulting in excessive waste. The average person throws away about 70 pounds of clothing every year, with a significant portion ending up in landfills, where it takes hundreds of years to decompose.
Economic Considerations:
The economic impact of fast fashion is complex and multifaceted. While the industry provides employment opportunities, particularly in developing countries, it also contributes to the decline of traditional textile industries and the displacement of skilled workers. The focus on low prices and mass production often leads to the outsourcing of manufacturing to countries with lower labor costs, leaving domestic industries struggling to compete.
Moreover, the fast fashion industry’s reliance on cheap labor and materials creates a race to the bottom, driving down prices and squeezing profit margins for smaller, more ethical brands. This creates a challenging environment for sustainable and ethical fashion practices to flourish.
Navigating the Complexities:
The impact of fast fashion is undeniably significant and warrants critical examination. While the industry offers convenience and affordability, its environmental, social, and economic consequences cannot be ignored. It is crucial to acknowledge the interconnectedness of these issues and to recognize that individual choices have a collective impact.
FAQs:
1. What are the key environmental concerns associated with fast fashion?
The key environmental concerns associated with fast fashion include the use of synthetic fibers like polyester, which are non-biodegradable and release microplastics into the environment, excessive water consumption for cotton production and dyeing processes, and significant carbon emissions throughout the supply chain.
2. How does fast fashion impact workers in the industry?
Fast fashion often leads to exploitative labor practices, with garment workers facing low wages, unsafe working conditions, and long hours. The industry’s focus on speed and efficiency prioritizes production over worker well-being.
3. What are the economic consequences of fast fashion?
Fast fashion can lead to the decline of traditional textile industries and the displacement of skilled workers. It also creates a challenging environment for sustainable and ethical fashion practices to thrive due to the focus on low prices and mass production.
4. What are some ways to reduce the impact of fast fashion?
Consumers can reduce the impact of fast fashion by buying fewer clothes, choosing sustainable and ethical brands, repairing and repurposing old garments, and supporting initiatives that promote circular fashion practices.
Tips for Sustainable Fashion Consumption:
1. Buy less, choose well: Resist the temptation to buy into every trend. Invest in high-quality, durable pieces that you can wear for years to come.
2. Prioritize quality over quantity: Opt for well-made garments from brands that prioritize ethical sourcing and production practices.
3. Embrace second-hand shopping: Explore vintage and thrift stores for unique pieces and give pre-loved clothes a new life.
4. Repair and repurpose: Extend the life of your clothes by repairing minor damages and getting creative with alterations and upcycling.
5. Support sustainable brands: Research and support brands that prioritize environmental and social responsibility in their operations.
6. Advocate for change: Educate yourself about the issues associated with fast fashion and advocate for policies that promote sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
The impact of fast fashion is a complex and multifaceted issue, demanding a holistic approach to address its environmental, social, and economic consequences. By fostering a greater understanding of the industry’s complexities and promoting sustainable consumption practices, we can work towards a more ethical and environmentally conscious fashion landscape. Individual choices, collective action, and policy changes are all crucial in mitigating the negative impacts of fast fashion and shaping a more sustainable future for the fashion industry.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Impact of Rapid Fashion Consumption: A Critical Examination. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!